Hello Android developers! Today, we’re diving into one of the most important security tools available for Android apps — the Play Integrity API. As app security becomes increasingly important, protecting your backend services from unauthorized access is crucial. In this guide, we’ll explore why you need the Play Integrity API, how to set it up, and provide code examples using Kotlin to get you started.
Why Do We Need the Play Integrity API?
When developing Android apps, especially those handling sensitive information like credit card details or private user data, ensuring that your app communicates with secure, legitimate devices is essential. The Play Integrity API helps you:
- Block unauthorized clients: It prevents attackers or hackers from accessing your backend resources by ensuring that only legitimate Android devices with your app can communicate with your backend.
- Protect API resources: The API helps safeguard your app’s API endpoints by verifying the integrity of the device accessing them.
- Improve app security: For applications dealing with sensitive operations, such as financial transactions, it’s a must-have to prevent attacks via rooted or compromised devices.
Think of the Play Integrity API as an extra layer of defense, ensuring that only verified, trusted devices can access your app’s backend services. This is especially useful if you manage apps with sensitive information, such as a banking or payment application, where user security is paramount.
How Does the Play Integrity API Work?

The Play Integrity API works by sending a nonce (a one-time string that helps prevent replay attacks) from your Android app to Google’s Play Integrity service. Google then checks the integrity of the device and the app, returning an encrypted response. This response must be validated on your backend to ensure it comes from a legitimate source.
Let’s break it down into simple steps:
- On your server, you set up the API and send a request to the app to generate a nonce.
- The app generates the nonce and sends it along with a Play Integrity request to Google’s service.
- Google checks the integrity of the app and device, then sends back a token.
- The app sends this token to your backend, where you verify the response.
- Based on the integrity check, you can decide whether to allow or block access to your app’s resources.
Setting Up the Play Integrity API in Google Play Console
Before you start coding, you need to enable the Play Integrity API in your Google Play Console and set up your Google Cloud project. Here’s how:
- Step 1: Go to your Play Console and navigate to Setup > App Integrity.
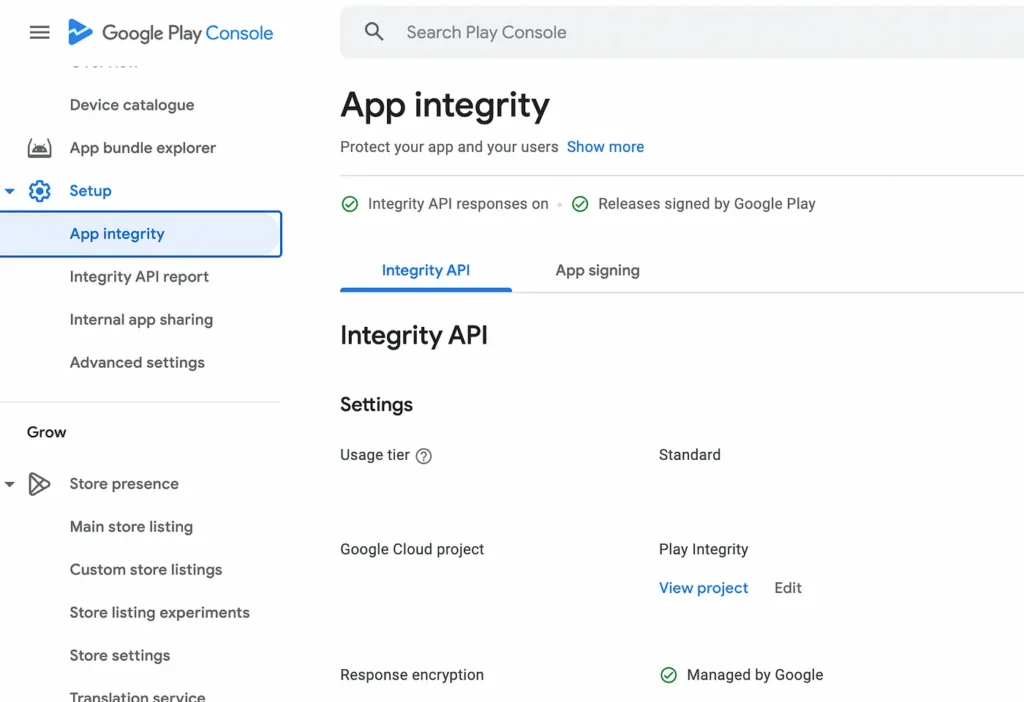
- Step 2: In the Integrity API tab, link your Google Cloud project. If you don’t have a project, create one.
- Step 3: Once linked, open the Google Cloud console and search for Play Integrity API.

- Step 4: Enable the API and create a Service Account with the necessary permissions. Download the JSON key file.

Now that we’ve configured the Play Integrity API, it’s time to move to the Android app implementation.
Server installation Maven Dependency;
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.apis</groupId>
<artifactId>google-api-services-playintegrity</artifactId>
<version>v1-rev20230514-2.0.0</version>
</dependency>
Setting Up the Play Integrity API in Your Android App
To start using the Play Integrity API in your Android app, you first need to add the necessary dependencies to your project. Add the following line to your build.gradle file:
implementation "com.google.android.play:integrity:1.1.0"Generating a Nonce
The nonce is a unique string that helps prevent replay attacks by ensuring that each request to the Play Integrity API is unique. Let’s create a function to generate this nonce. The nonce must be URL-safe, encoded in Base64, and between 16 to 500 characters long.
private fun generateNonce(): String {
val length = 50
val allowedChars = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789"
return (1..length)
.map { allowedChars.random() }
.joinToString("")
}
Explanation: This function generates a random string that is 50 characters long. You can modify the length parameter to suit your needs.
Requesting an Integrity Token
Now that we have our nonce, it’s time to request the integrity token from Google’s Play Integrity service. Here’s how you can do it in Kotlin:
val integrityManager = IntegrityManagerFactory.create(context)
val integrityTokenResponseTask = integrityManager.requestIntegrityToken(
IntegrityTokenRequest.builder()
.setNonce(generateNonce()) // Attach the generated nonce
.setCloudProjectNumber(CLOUD_PROJECT_NUMBER) // Replace with your Google Cloud Project Number
.build()
)
integrityTokenResponseTask.addOnSuccessListener { integrityTokenResponse: IntegrityTokenResponse ->
val integrityToken = integrityTokenResponse.token()
Log.d("Play Integrity Token", integrityToken)
// Send the token to your backend for validation
}
.addOnFailureListener { e: Exception ->
Log.e("Play Integrity API Error", "Error generating token: ${e.message}")
}
Important: Replace CLOUD_PROJECT_NUMBER with the number from your Google Cloud project.
Once the token is generated, it must be sent to your backend, where you’ll validate its authenticity and decide whether to grant or deny access to your app’s resources based on the integrity check.
Validating the Integrity Token on Your Backend
After receiving the token from your Android app, you need to validate it on your backend. Here’s an example of how you might validate the token using Node.js or Java:
// In your backend, validate the integrity token
const { google } = require('googleapis');
const playintegrity = google.playintegrity('v1');
async function validateToken(token) {
const res = await playintegrity.playIntegrity().decodeIntegrityToken({
requestBody: {
integrityToken: token
}
});
// Parse the response and check for device integrity
console.log(res.data);
}
If the integrity check fails (e.g., if the device is rooted or compromised), you can block access to your app or prevent certain actions like making purchases or accessing sensitive data.
Conclusion: Why Play Integrity API Is Crucial
The Play Integrity API is an essential tool for ensuring your Android app’s security, especially if you handle sensitive information or require strict device validation. By integrating this API, you protect your backend from unauthorized access, improve overall app security, and provide a safer user experience.
Now that you know how to set it up, it’s time to secure your app! Start implementing the Play Integrity API today, and take your app’s security to the next level.
Happy coding! 😊
Source: Play Integrity API Documentation
Did you like this article?
You can subscribe to my newsletter below and get updates about my new articles.