While developing secure android applications, SSL Pinning is a security measure that ensures that the application communicates with trusted servers only by verifying SSL certificates. This is very important to protect sensitive data from man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. Otherwise, hackers who access your application with malware can cause serious damage to you. In this article, we will look at how to implement SSL Pinning on Android using OkHttp and Ktor.
What is SSL Pinning?
SSL is actually encrypted certificates as a secure socket layer.
SSL Pinning allows you to send/read the data you send and receive while communicating with your Android application’s backend servers by encrypting it.
While sending this data, we encrypt the secure SSL with TLS and provide communication.
When our server sees that we have come with a secure vehicle, it gives us the necessary information flow.
Of course, this security measure can be easily broken by a hacker in Android applications.
Before doing this, if you have any questions like how to create an android application? How to create a service structure? Please visit here to learn them.
Can SSL Pinning be Bypassed?
Yes, Our aim is only to make the hackers’ job difficult (to increase the work they will do in 1 step to 10 steps), otherwise it is normal for every security measure to be broken.
Implementing SSL Pinning with OkHttp
OkHttp is a popular networking library used in Android. To implement SSL Pinning with OkHttp, you need to obtain the certificate of the server you are communicating with.
Note: Since Retrofit is a library built on Okhttp, you can also do this with Retrofit or similar tools.
Export Your Server’s Certificate
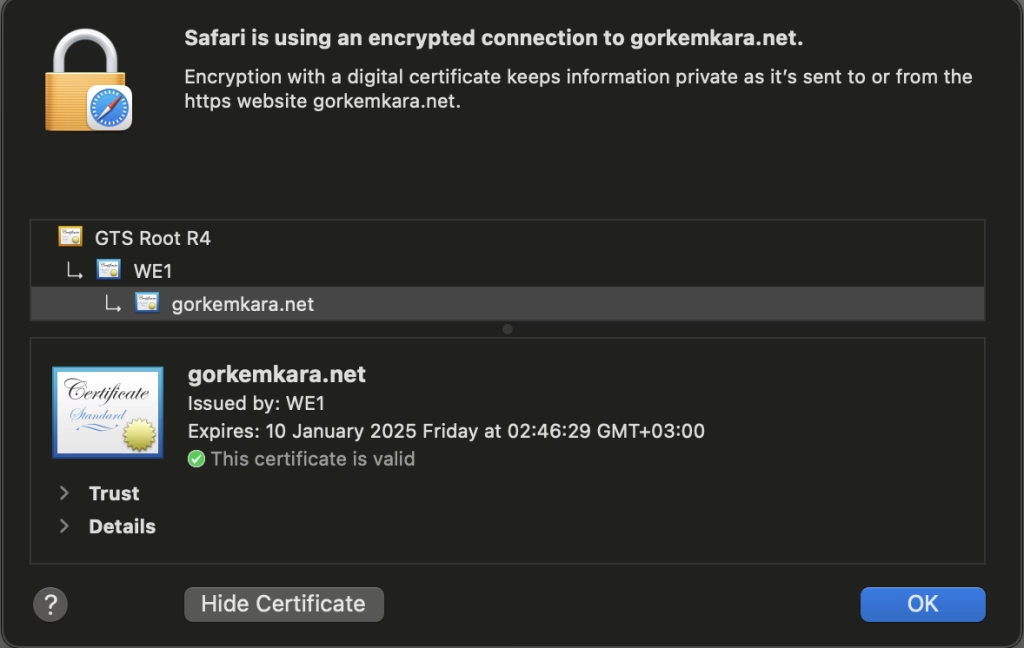
Go to your server address in a browser. This could be something like api.server.com.
Then click on the lock (secure) icon to the left of the URL in the browser. In the window that opens, click on the “Certified valid” or “Show certificate” buttons. If you are using Windows, you can go to the detail page in the window and save it by saying copy to file.
t
i
Click on the certificate’s logo or drag it to the desktop and download it as a .cert file.
If you can’t download the “cert” file this way, try downloading it using online tools. For example, I found a site for you. Click here.
Convert Certificate To Pem
We want to convert the .cert file to .pem file and obtain the base64 code. And as I will explain below, we will pull this from the server and perform a fully secure ssl pinning.
Install OpenSSL
openssl converts the .cert file to .pem file and allows us to obtain base64 code.
Download openssl for windows from: https://openssl-library.org/source/
For macos, type the following command in terminal:
brew install openssl.cert to pem
Open the command window. Go to the directory where the .cert file you downloaded is located and run the following command.
openssl x509 -in CERT_TO_DOWNLOANDED.crt -out certificate.pem -outform PEMNote: Remember to replace the certificate file name in the command with your own.
Right click on the resulting .pem file and open it with a text editor. And here is the base64 of the certificate.
Add this base64 code as a STRING to the “initial setup api” or firebase remote config from the apis you use for your application and complete the retrieval processes from there.
SSL Certificate Pinning in Okhttp
Let’s add the certificate you received from the remote server as a string to okhttp.
Create X509Certificate
Certificates are known as X509Certificate in Android and you can decode a string certificate to it.
X509Certificate x509Certificate = okhttp3.tls.Certificates.decodeCertificatePem(cert);You can give the base64 string you received from your remote server to the cert parameter here.
Add SSL Certifacete to Okhttp
Install Okhttp in a standard way.
OkHttpClient.Builder okHttpClient = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
// establish connection with server
.connectTimeout(CONNECTION_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
// time between each byte read from server
.readTimeout(READ_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
// time between each byte sent to server
.writeTimeout(WRITE_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.retryOnConnectionFailure(true)
.addNetworkInterceptor(interceptor)
.addInterceptor(httpLoggingInterceptor);Now add ssl pinning.
X509Certificate x509Certificate = okhttp3.tls.Certificates.decodeCertificatePem(cert);
okHttpClient.sslSocketFactory(
sslSocketFactory: new HandshakeCertificates.Builder()
.addTrustedCertificate(x509Certificate)
.build().sslContext().getSocketFactory(),
trustManager: handshakeCertificates.trustManager()
)
okHttpClient.build()Bypass if SSL Pinning fails
You will receive an SSL error when you first go to your remote server. If you encounter any errors, you need to bypass SSL by writing the code below.
if(x509Certificate != null){
okHttpClient.sslSocketFactory(
sslSocketFactory: new HandshakeCertificates.Builder()
.addTrustedCertificate(x509Certificate)
.build().sslContext().getSocketFactory(),
trustManager: handshakeCertificates.trustManager()
)
}else {
try {
final TrustManager[] trustAllCerts = new TrustManager[]{
new X509TrustManager() {
@Override
public void checkClientTrusted(java.security.cert.X509Certificate[] chain, String authType) {
}
@Override
public void checkServerTrusted(java.security.cert.X509Certificate[] chain, String authType) {
}
@Override
public java.security.cert.X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() {
return new java.security.cert.X509Certificate[]{};
}
}
};
final SSLContext sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("SSL");
sslContext.init(null, trustAllCerts, new java.security.SecureRandom());
final SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory = sslContext.getSocketFactory();
okHttpClient.sslSocketFactory(sslSocketFactory, (X509TrustManager) trustAllCerts[0]);
okHttpClient.hostnameVerifier((hostname, session) -> true);
} catch (Exception exception) {
Logger.w(exception);
CrashlyticsUtil.getInstance().setAppCrashError(exception);
}
}In this way, when you implement all the code correctly, your application will be more secure.
Don’t be afraid of your SSL certificate being stolen because the method I showed you is a publicly verifiable SSL certificate.
SSL Pinning Security Considerations
- Certificate Expiration: Certificates expire over time, and if the pinned certificate is outdated, your app will fail to communicate with the server. Keep your certificates updated regularly.
- Multiple Certificates: If your server rotates certificates, consider pinning multiple certificates.
- Debugging: During development, SSL Pinning can make debugging difficult. Consider disabling SSL Pinning for debug builds, as shown above, to facilitate easier testing.
Conclusion
We have done a study to make your application more secure by doing SSL Pinning. Although this is sometimes necessary for security, it makes it difficult for us while developing, so please do not forget to bypass ssl with BuildConfig.DEBUG after you see that your code is working.
Did you like this article?
You can subscribe to my newsletter below and get updates about my new articles.